CEIC Leading Indicator for Brazil lowest in 16 months


The CEIC Leading Indicator for Brazil fell below 90 in October, for the first time since June 2020. The non-smoothed indicator stood at 89.9 compared to 93.8 in September. This also marked the fourth consecutive month of decline for the indicator, suggesting that the economy is currently in a downturn phase. Continuously rising consumer inflation and an energy crisis coupled with a weak Brazilian real has hampered the recovery prospects of Latin America’s largest economy.
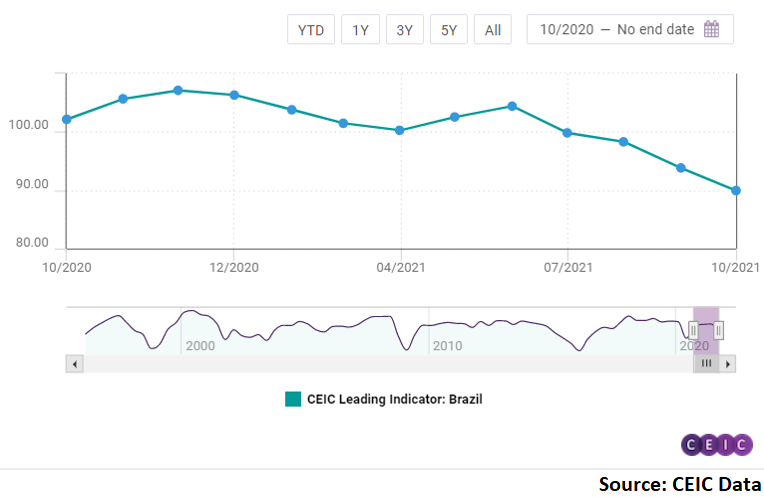
Rising inflation expectations have been at the core of the underwhelming performance of the CEIC Leading Indicator in October. FGV’s consumer inflation expectation indicator jumped to 8.9 from 7.7 in September, suggesting that the already double digit inflation in the country might rise even further, despite the interest rate hike undertaken by the Central Bank in the last week of October. Manufacturing confidence declined by 1.2pp m/m in October, to 5.4%. The booming construction sector might also slow down in the coming months, as the expectation to purchase inputs index declined slightly to 55 in October from 55.1 in September 2021. The performance of the equity market index Ibovespa was also in line with the struggling economy as it closed October at its weakest in a year, at 103,500.7. International crude oil prices averaged USD 82.1 per barrel in October, rising above USD 80 per barrel for the first time in 7 years.
In the long run, Brazil’s economic growth may also moderate, as the smoothed CEIC Leading Indicator fell by 3.7 points to 91.8, below the neutral value of 100. The smoothed indicator has been declining since January 2021, suggesting that the immediate peak of Brazil’s post COVID-19 recovery has passed at the beginning of the year.
More on the CEIC Leading Indicator here
Further data and analysis on Brazil’s economy are available on the CEIC Brazil Economy in a Snapshot – Q3 2021 report.